🙂 서론
제가 느끼기엔 properties 보다는 yaml 파일이 더 가독성이 좋아 관리하기 쉽다고 생각합니다.
설정 파일을 불러와 객체를 만들 때 보통 @PropertySource 애노테이션을 사용하지만, default로 yaml을 읽지 못합니다.
그렇다고, yaml과 properties를 같이 사용하는 건 통일성이 없고, 그럴 필요가 없다 생각됩니다.
그렇기 때문에 이를 yaml 파일을 읽을 수 있도록 설정한 방법을 정리해봅니다.
😛 본론
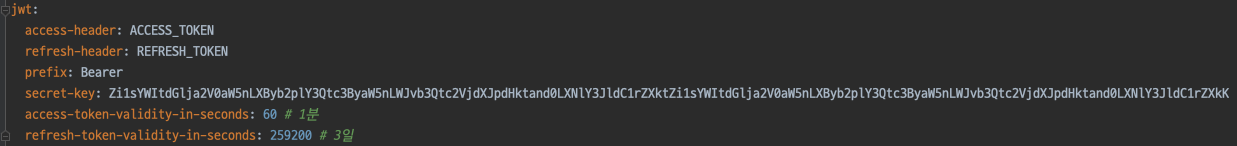
가져올 yml 파일의 설정 값입니다.
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@ConstructorBinding
@ConfigurationProperties(value = "jwt")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:application.yml", factory = YamlPropertySourceFactory.class)
public class JwtProperties {
private final String accessHeader;
private final String refreshHeader;
private final String prefix;
private final String secretKey;
private final Integer accessTokenValidityInSeconds;
private final Integer refreshTokenValidityInSeconds;
}바인딩할 클래스입니다.
property의 네이밍으로 맵핑되기 때문에 네이밍을 맞춰주시면 됩니다.
적용한 애노테이션을 하나씩 살펴보겠습니다.
@ConfigurationProperties(value = "jwt")
*. properties 혹은 *. yaml 파일에 있는 property를 자바 클래스에 바인딩하여 사용할 수 있게 해주는 애노테이션.
저는 properties 중 jwt 부분을 가져온다고 명시해주었습니다.
(바인딩 방식은 setter 혹은 생성자 방식이 있습니다.)

@ConstructorBinding
생성자 방식으로 바인딩할 때 사용하는 애노테이션.
@RequiredArgsConstructor
설정 값을 임의로 변경하지 못하도록 final로 선언하여, 생성자를 만들어줍니다. (final 명시된 property만 추가됩니다.)
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:application.yml", factory = YamlPropertySourceFactory.class)
value : 어느 파일을 읽어올지 지정해줍니다.
factory : yaml 파일을 읽어오기 위해선 Coustom Factory를 만들어서 정의해주어야 합니다.
public class YamlPropertySourceFactory implements PropertySourceFactory {
@Override
public PropertySource<?> createPropertySource(@Nullable String name, EncodedResource resource) {
Properties yamlProperties = loadYamlProperties(resource);
String sourceName = StringUtils.hasText(name) ? name : resource.getResource().getFilename();
return new PropertiesPropertySource(Objects.requireNonNull(sourceName), Objects.requireNonNull(yamlProperties));
}
private Properties loadYamlProperties(EncodedResource resource) {
YamlPropertiesFactoryBean factory = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
factory.setResources(resource.getResource());
return factory.getObject();
}
}yaml 파일을 읽을 수 있도록 Custom Factory 만든, YamlPropertySourceFactory.class 구현 코드입니다.
'jwt' 정보 외에도 yaml 파일을 읽고 싶다면, 만든 factory를 재사용할 수 있습니다.
테스트 코드
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = JwtProperties.class)
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:application.yml", factory = YamlPropertySourceFactory.class)
class JwtPropertiesTest {
@Autowired
private JwtProperties jwtProperties;
@Test
@DisplayName("yml - jwt 설정파일 체크")
void jwtPropertiesCheck() {
// given
// when
// then
assertAll(
() -> assertThat(jwtProperties.getAccessHeader()).isEqualTo("ACCESS_TOKEN")
, () -> assertThat(jwtProperties.getRefreshHeader()).isEqualTo("REFRESH_TOKEN")
, () -> assertThat(jwtProperties.getPrefix()).isEqualTo("Bearer")
, () -> assertThat(jwtProperties.getAccessTokenValidityInSeconds()).isEqualTo(60)
, () -> assertThat(jwtProperties.getRefreshTokenValidityInSeconds()).isEqualTo(259200)
, () -> assertThat(jwtProperties.getSecretKey()).isNotEmpty());
}
}설정 파일을 제대로 가져왔는지 테스트코드까지 작성하여 확인하면 끝이 납니다.
🥸 결론
설정파일을 클래스로 바인딩해서 사용하면 필요한 곳마다 불러올 필요가 없기 때문에, 괜찮은 방법인 것 같습니다.
참고
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-yaml-propertysource
@PropertySource with YAML Files in Spring Boot | Baeldung
A quick and practical guide to handling YAML files with @PropertySource in Spring Boot.
www.baeldung.com
https://vsh123.github.io/spring%20boot/spring-boot-yml/
spring boot yml에 있는 상수 값 불러오기
상수 값들을 yml파일로 관리하고 싶을 때? 다음과 같이 두 가지 방법으로 진행이 가능하다.
vsh123.github.io
'JVM > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] Exception 어떻게 처리할까? (0) | 2022.06.26 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] enum으로 @Secured 권한 관리 (0) | 2022.06.18 |
| [SPRING] 스프링 MVC 구조? (DispatcherServlet?) (0) | 2022.04.22 |
| [SPRING] @Valid @Validated 사용하기 - java bean validation (0) | 2022.03.26 |
| [SPRING] @Valid 어떻게 동작할까 - java bean validation (0) | 2022.03.26 |
